Why Do Sulfur and Chloride Liquids Have Such An Adverse Effect On pH Sensors?
Chlorides and sulfur-based products can have a significant effect on pH sensors because they can cause reference poisoning. Reference poisoning occurs when impurities in the sample, such as chlorides or sulfur-based products, react with the reference electrode and change its voltage. This can cause the sensor to produce inaccurate readings, and it can even lead to the failure of the sensor.
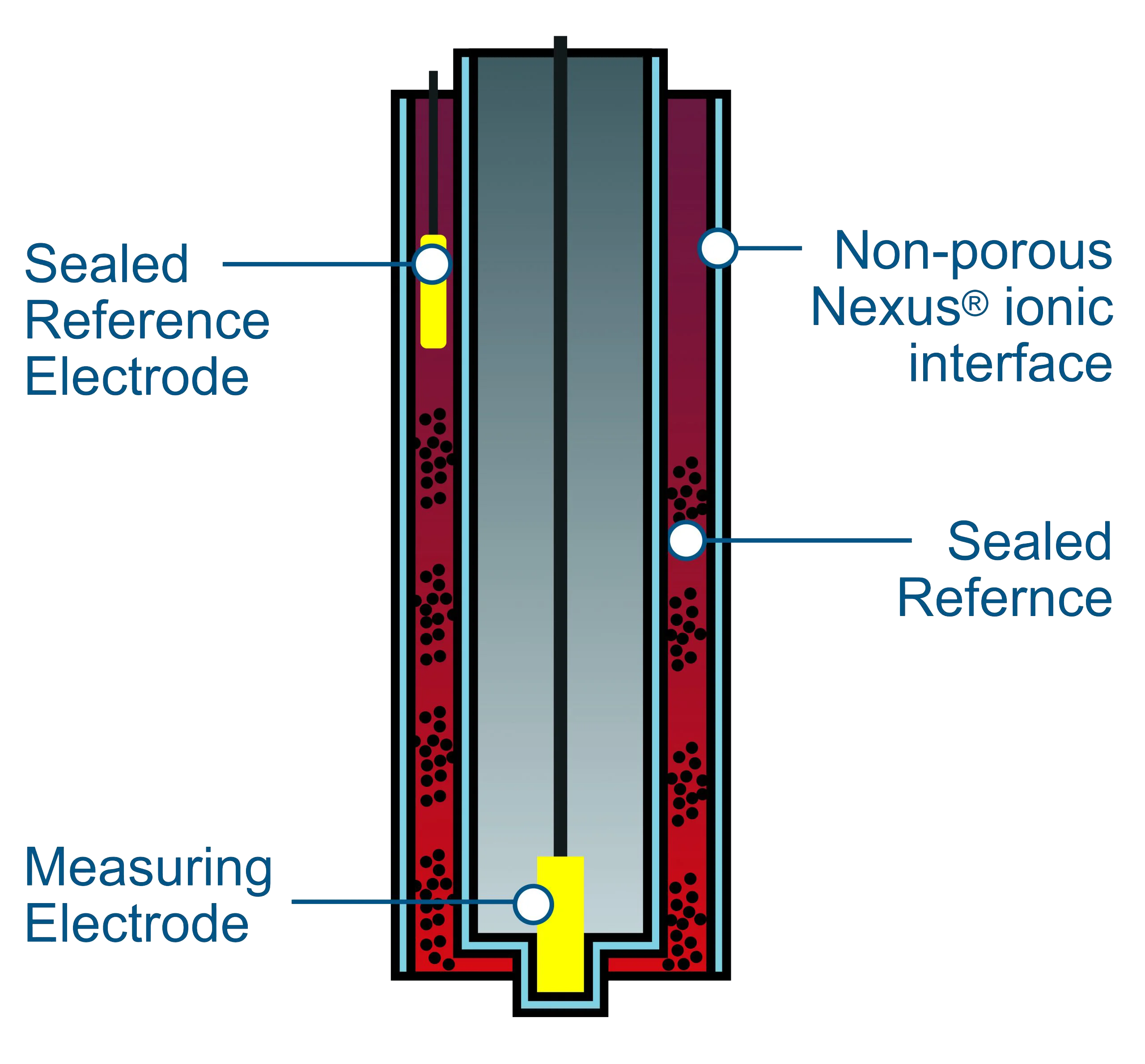
The reference electrode in a pH sensor is typically made of a metal, such as silver or silver chloride, that is in contact with a solution of known pH. This solution, called the reference electrolyte, provides a stable voltage that the sensor can use to measure the pH of the sample. The reference electrode is connected to the sensor through a porous glass or ceramic junction, which allows ions to flow between the reference electrolyte and the sample.
When chlorides or sulfur-based products are present in the sample, they can react with the reference electrode and change its voltage. Chlorides, for example, can react with the silver in the reference electrode to form silver chloride, which can change the voltage of the reference electrode. Similarly, sulfur-based products can react with the reference electrode and change its voltage. These reactions can cause the reference electrode to produce inaccurate voltages, which can in turn cause the sensor to produce inaccurate pH readings.
Reference poisoning can be particularly problematic for sensors that are used in industrial or environmental applications, where samples may contain high levels of chlorides or sulfur-based products. In these cases, it is important to use high-quality reference electrodes that are designed to resist reference poisoning and to keep them clean and well-maintained. It is also important to use a reference electrolyte that is compatible with the sample, to minimize the risk of reference poisoning.
In addition, using pH sensors with built-in reference poisoning protection is an option to minimize the adverse effect of chlorides and sulfur-based products on pH sensors. These sensors often use a reference electrolyte that is less likely to react with chlorides or sulfur-based products, and they may also have a protective coating that can help to prevent reference poisoning.
In summary, Chlorides and sulfur-based products can have a significant effect on pH sensors because they can react with the reference electrode, causing it to produce inaccurate voltages. This can cause the sensor to produce inaccurate pH readings and can even lead to failure of the sensor. To prevent reference poisoning, it is important to use high-quality reference electrodes, keep them clean and well-maintained, and use reference electrolyte that is compatible with the sample.